Public Data Access Overview / TNG50 Milky Way+Andromeda (MW/M31) Sample
This is the special data access page for the TNG50 Milky Way + Andromeda sample, as presented in Pillepich+ (2024). Here you can download the full snapshot cutouts of each of the [198] MW/M31-like galaxies, at $z=0$ as well as all higher redshift snapshots. Three data products are available: (i) a catalog of the sample, including many physical properties of each MW/M31-like galaxy, (ii) a catalog of the satellite galaxies surrounding each MW/M31-like central, and (iii) individual snapshot cutouts of the stars, dark matter, gas, and supermassive black holes which reside in, and around, each galaxy.
We request that any publication making use of data from this page should cite Pillepich+ (2024). Any publication making use of specific datasets in the tables below should also cite the corresponding publication(s).
Table of Contents
- 1. Overview and Visuals
- 2. Local Group and LMC/SMC Analogs
- 3. Data Products
- 4. TNG50 Papers Studying the MW/M31 Sample
- 5. Landscape of LCDM Simulations of MW/M31 Analogs
Overview and Visuals

There are five visualization galleries showcasing the diversity and heterogeneity of the TNG50 MW/M31 galaxy sample.
- Pillepich+ (2024) of the stellar light morphologies and structure of galactic disks.
- Pillepich+ (2024) of the physical properties of the gaseous and stellar galactic disks of the sample.
- Ramesh+ (2023a) of the physical properties of the circumgalactic medium (CGM) of the sample: gas density, temperature, pressure, entropy, HI, metallicity, OVI, and X-rays.
- Pillepich+ (2021) of Fermi/eROSITA-like bubbles driven by AGN feedback in the CGM of many galaxies in the sample.
- Ramesh+ (2023b) of the existence, abundance, and distribution of small, cool clouds in the CGM of the Milky Way-like galaxies of the sample.
Local Group and LMC/SMC Analogs
In Pillepich+ (2024) we identified three pairs of galaxies in TNG50 which resemble the Local Group. The SubhaloIDs of the LG-like pairs are: 400973+400974; 425719+580406; and 454171+454172, which are pictured below in gas temperature, X-ray emission, and gas column density projections, respectively.
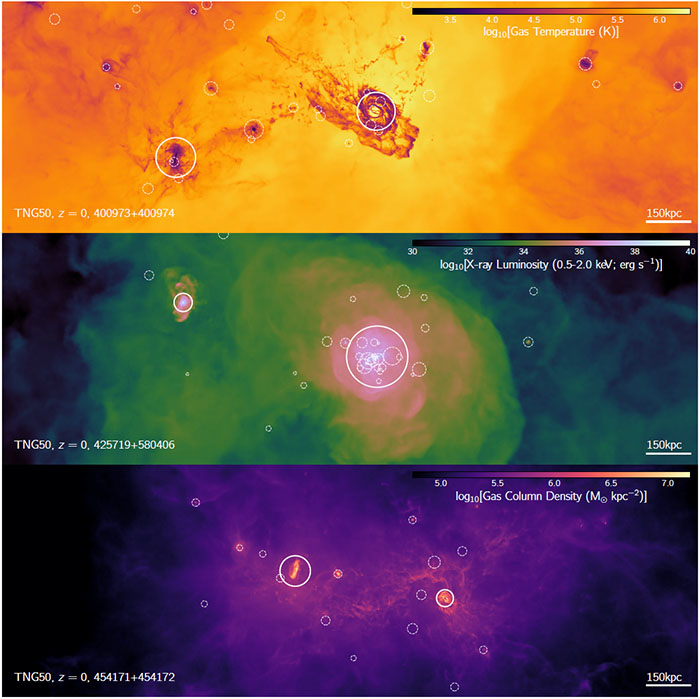
We note that there is also one system with three MW/M31-like galaxies within 500 − 1000 kpc from each other, with SubhaloIDs 414917, 414918, and 528836.
Among the 77 MW/M31-like galaxies surrounded by at least a SMC-like satellite, and among the 42 galaxies surrounded by at least a LMC-like satellite, 4 in each category have the SMC- (LMC)-like satellite currently within a distance, and with tangential and radial velocities, comparable to the actual Magellanic Clouds. These systems have the following SubhaloIDs pairs: 342447+342458; 400973+400981; 411449+411470; 502995+502998; and 358609+358614; 414918+414921; 467415+467418; 471248+471251.
We also highlight six galaxies as our closest Milky Way analogs. These are Subhalo IDs 516101, 535774, 538905, 550149, 552581, and 566365. We also highlight one galaxy as our closest Andromeda analog, with Subhalo ID 432106. In all cases, their stellar disk properties, including disk lengths and total stellar mass, are within the observational estimates for the Galaxy and M31, respectively.
Data Products
MW/M31 Catalog
The "TNG50 MW/M31-like catalog" includes the Subhalo IDs, and many physical properties, for each of the [198] galaxies in the sample, at $z=0$. Given the SubfindID, many additional properties can be obtained from the original catalog files of the simulation.
- Download TNG50 MW/M31-like Catalog (single HDF5 file, ~100 KB)
| Dataset | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SubfindID | -- | The z=0 Subfind ID of the galaxy, within the TNG50 simulation (always at z=0, i.e. does not change for higher redshift cutouts). |
| FlagCentral | -- | Flag is 1 if the galaxy is the central i.e. the first/main/most massive Subhalo object of its FoF halo. |
| FlagDiskyVisual | -- | Flag is 1 if the galaxy appears disky and with spiral arms based on a visual inspection of 3-band stellar light images, both face-on and edge-on. |
| FlagDiskyMinor2Major | -- | Flag is 1 if the stellar-mass minor-to-major axis ratio is smaller than a certain value: $c/a \le 0.45$. Based on galaxy shapes from Pillepich+ (2019). |
| FlagDisky | -- | Flag is 1 if (FlagDiskyVisual==1 OR FlagDiskyMinor2Major==1). That is, this flag is 1 if the galaxy has a stellar disky morphology either based on visual inspection or based on the stellar axis ratios. |
| FlagIsolated | -- | Flag is 1 if there is no galaxy with $M_*(<30{\rm kpc})\ge 10^{10.5}\,\rm{M}_\odot$ within 500 kpc distance and if $M_{\rm 200c,host} < 10^{13}\,\rm{M}_\odot$. |
| FlagMstars | -- | Flag is 1 if $M_*(<30{\rm kpc}) = 10^{10.5-11.2}\,\rm{M}_\odot$. |
| FlagM200c | -- | Flag is 1 if $M_{\rm 200c,host} = 6\times10^{11}-2\times10^{12}\,\rm{M}_\odot$. |
| FlagNoVirgo | -- | Flag is 1 if there is no FoF/Group halo with $M_{\rm 200c} \gtrsim 10^{14}\,\rm{M}_\odot$ within 10 Mpc distance. For TNG50, this includes a constraint on the two most massive systems in the box at $z=0$. |
| FlagS0 | -- | Flag is 1 if the galaxy appears as an S0 per visual inspection, namely it has a disky stellar morphology but with no manifest spiral arms. |
| FlagBarredZana22 | -- | Flag is 1 if the galaxy has a bar according to Zana+ (2022). |
| FlagBarredRosas22 | -- | Flag is 1 if the galaxy has a bar according to Rosas-Guevara+ (2020), Rosas-Guevara+ (2022). |
| FlagMWM31 | -- | Flag is 1 if (FlagDisky==1 & FlagMstars==1 & FlagIsolated==1). This is the fiducial selection of this sample. All entries in this catalog should be equal to 1. Other more restrictive selections can be imposed using the provided additional flags. |
| StellarMass_30kpc | $\rm{M}_\odot$ | Galaxy stellar mass evaluated by summing up the mass of all stellar particles that are gravitationally bound according to Subfind and within a 3D radius of 30 kpc from the galaxy center. This is our fiducial definition. |
| StellarMass_2rh | $\rm{M}_\odot$ | Galaxy stellar mass evaluated by summing up the mass of all stellar particles that are gravitationally bound according to Subfind and within a 3D radius of twice the stellar half mass radius. This is equivalent to SubhaloMassInRadType[4] in the official Subfind catalogs. |
| StellarMass_all | $\rm{M}_\odot$ | Galaxy stellar mass evaluated by summing up the mass of all stellar particles that are gravitationally bound according to Subfind, with no distance limit. This also includes the mass in e.g. the stellar halo. |
| HaloMass_M200c | $\rm{M}_\odot$ | Total halo mass in terms of the spherical-overdensity measure $M_{\rm 200c}$. For non central galaxies, this is the halo mass of the host. |
| HaloMass_Mdyn | $\log \rm{M}_\odot$ | Total halo mass obtained by summing up the mass of all particles and cells that are gravitationally bound according to Subfind. |
| SFR_inst | $\rm{M}_\odot / \rm{yr}$ | Star formation rate of the galaxy based on the instantaneous SFR of the gas, i.e. sum of the individual star formation rates of all gravitationally-bound gas cells in this galaxy. It is equivalent to SubhaloSFR in the official Subfind catalogs. |
| SFR_50Myr | $\rm{M}_\odot / \rm{yr}$ | Time-averaged star formation rate of the galaxy including stars within a 3D aperture of 30 kpc, based on the stellar particles actually produced over the last 50 million years and using their initial mass at birth; as in Pillepich+ (2019). |
| DiskScaleLength | $\rm{kpc}$ | Exponential disk length of the galaxy obtained by fitting the stellar mass surface density of stellar particles in disky orbits between 1 and 4 times the stellar half mass radius. See errorbars and fitting procedure in Sotillo+ (2022) and Sotillo+ (2023). |
| DiskScaleHeightThin_8kpc | $\rm{pc}$ | Thin stellar disk height of this galaxy obtained by fitting the vertical stellar mass density distribution of disk stars with a double squared hyperbolic secant functional form in an annulus of 7-9 kpc from the center. See errorbars, fitting procedure, and additional different measurements in Sotillo+ (2022) and Sotillo+ (2023). |
| DiskScaleHeightThick_8kpc | $\rm{pc}$ | Same as above, for the thick component. Thin and thick disk heights here are meant as geometrical. |
| SMBH_Mass | $\rm{M}_\odot$ | Mass of the central (i.e. most massive) SMBH in this galaxy. The measurement is based on the PartType5/BH_Mass of the snapshot data. For MW/M31-like galaxies, this mass is equivalent to SubhaloBHMass in the official Subfind catalog. |
| SMBH_AccretionRate | $\rm{M}_\odot / \rm{yr}$ | Instantaneous gas mass accretion rate into the SMBH of this galaxy, based on SubhaloBHMdot from the official Subfind catalog. |
| SMBH_EddingtonRatio | -- | Instantaneous Eddington ratio of the SMBH of this galaxy. |
| SMBH_FeedbackMode | -- | Value is 0 if the SMBH of this galaxy is in thermal feedback mode, or 1 if it is exercising kinetic feedback mode (see Weinberger+ (2017)). |
MW/M31 Satellites Catalog
The "TNG50 MW/M31-like Satellites catalog" includes the Subhalo IDs, and many physical properties, for all the satellite galaxies surrounding each of the [198] MW/M31-like centrals in the sample. There are a total of [1237] such satellites, and they have been studed in Engler+ (2021) and Engler+ (2023).
- Download TNG50 MW/M31-like Satellites Catalog (single HDF5 file, ~100 KB)
| Dataset | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SubfindIDSat | -- | The z=0 Subfind ID of the satellite galaxy, within the TNG50 simulation. |
| SubfindIDHost | -- | The z=0 Subfind ID of the host (parent) galaxy of this satellite, within the TNG50 simulation. These can only take the values of the SubhaloIDs of the corresponding catalog. The host is the closest main galaxy. |
| DistanceToHost3D | $\rm{kpc}$ | Three-dimensional distance of the satellite galaxy to the host (parent) galaxy. |
| DistanceToHost2D | $\rm{kpc}$ | Two-dimensional distance of the satellite galaxy in a random projection to the host galaxy (along z axis of the simulation box). |
| 3DVelocityRelToHost | $\rm{km/s}$ | Three-dimensional relative velocity of the satellite galaxy with respect to the host galaxy. |
| LoSVelocityRelToHost | $\rm{km/s}$ | Line-of-sight relative velocity of the satellite galaxy with respect to the host galaxy, in a random projection (along z axis of the simulation box). |
| StellarMass_2rh | $\log \rm{M}_\odot$ | Galaxy stellar mass evaluated by summing up the mass of all stellar particles that are gravitationally bound according to Subfind and within a 3D radius of twice the stellar half mass radius. This is equivalent to SubhaloMassInRadType[4] in the official subhalo catalogs. |
| Magnitude_VBand | $\rm{mag}$ | Absolute V-band Buser's magnitude of the satellite galaxy based on the summed-up luminosities of all the gravitationally-bound stellar particles (Vega magnitudes), from the GFM_StellarPhotometrics field of the official snapshot data. |
| Magnitude_rBand | $\rm{mag}$ | As for Magnitude_VBand, but in the SDSS r band (AB magnitudes). |
| Mdyn | $\rm{M}_\odot$ | Total halo mass of the satellite galaxy obtained by summing up the mass of all particles and cells that are gravitationally bound according to Subfind. |
| GasMass_2rh | $\log \rm{M}_\odot$ | Total gas mass of the satellite galaxy evaluated by summing up the mass of all stellar particles that are gravitationally bound according to Subfind and within a 3D radius of twice the stellar half mass radius. This is equivalent to SubhaloMassInRadType[0] in the official subhalo catalogs. |
| HIGasMass_2rh | $\log \rm{M}_\odot$ | Atomic hydrogen mass of the satellite galaxy evaluated by summing up the HI mass of all gas cells that are gravitationally bound according to Subfind and within a 3D radius of twice the stellar half mass radius. This is based on the 'GK' HI+H2 partitioning by Popping+ (2019).. |
| H2GasMass_2rh | $\log \rm{M}_\odot$ | As for HIGasMass_2rh but for the molecular hydrogen.. |
| HalfLightRadius2D_VBand | $\rm{kpc}$ | Two-dimensional circularized stellar half-light radius of the satellite galaxy in the V-band, from a face-on projection. Based on Pillepich+ (2019). |
| StellarVelDisp_3D | $\rm{km/s}$ | Three-dimensional standard deviation of the velocities of all stellar particles of the satellite galaxy within twice the stellar half-mass radius weighted by their respective stellar mass. |
| SurfaceBrightness2D_rBand | $\rm{mag / arcsec^2}$ | Two-dimensional surface brightness of the satellite galaxy in the SDSS r band (see above). |
| Vmax | $\rm{km/s}$ | Maximum of the circular velocity profile of the satellite galaxy, accounting for all matter components. |
| SFActivity | -- | Flag denoting the star-formation activity of the satellite gaalxy: 1, 0, -1 for star-forming, quenched and green-valley galaxies, respectively. This is based on Pillepich+ (2019) and on the distance from the ridge of the star-forming main sequence. |
| t10 | $\rm{Gyr}$ | Stellar assembly time $\tau_{10}$, i.e. lookback time when the galaxy assembled 10 per cent of its $z=0$ stellar mass. Based on Joshi+ (2021). |
| t50 | $\rm{Gyr}$ | As above for t10, but giving the lookback time when the galaxy assembled 50 per cent of its $z=0$ stellar mass. |
| t90 | $\rm{Gyr}$ | As above for t10, but giving the lookback time when the galaxy assembled 90 per cent of its $z=0$ stellar mass. |
MW/M31 Cutout Data
For each of the [198] MW/M31-like galaxies at $z=0$ we have created "cutouts" of the TNG50 snapshot data, selecting all particles and gas cells within a cube of ±400 comoving kpc from the center of each galaxy. These cutouts are available at $z=0$ as well as all previous snapshots up to $z=7$ (snapshot #11), in all cases keeping the comoving cutout size fixed, and following the position of the main progenitor in time. Each cutout is ~ 500 MB to ~ 2 GB in size.
These cutouts have several key advantanges: (i) they are complete out to a distance of ±400 ckpc, such that gas, stars, dark matter, satellites, and so on can be studied out to the virial radii of these galaxies and beyond; (ii) they contain many additional fields not available in the normal TNG snapshots; these include neutral and molecular hydrogen gas masses, in-situ versus ex-situ stellar flags, and so on - see below; (iii) they contain all the Monte Carlo tracers within each cutout.
Clicking on an image in the following table will download a single HDF5 cutout file at $z=0$. The Subhalo ID itself links to the corresponding page in the API, where you will find the complete download links for all redshifts/snapshots, from 11 to 99 (inclusive).

342447
$M_\star$ = 10.87

358609
$M_\star$ = 10.81

372754
$M_\star$ = 11.09

372755
$M_\star$ = 10.74

388544
$M_\star$ = 11.09

392277
$M_\star$ = 10.58

400973
$M_\star$ = 11.04

400974
$M_\star$ = 10.48

402555
$M_\star$ = 11.03

411449
$M_\star$ = 11.12

414917
$M_\star$ = 11.08

414918
$M_\star$ = 10.32

416713
$M_\star$ = 10.95

419618
$M_\star$ = 10.60

421555
$M_\star$ = 10.95

422754
$M_\star$ = 10.81

424288
$M_\star$ = 10.86

425719
$M_\star$ = 10.94

427211
$M_\star$ = 10.99

428177
$M_\star$ = 10.90

429471
$M_\star$ = 10.99

430864
$M_\star$ = 10.92

432106
$M_\star$ = 11.09

433289
$M_\star$ = 11.16

435752
$M_\star$ = 10.93

436932
$M_\star$ = 11.03

438148
$M_\star$ = 11.13

439099
$M_\star$ = 10.96

440407
$M_\star$ = 10.82

441709
$M_\star$ = 11.00

443049
$M_\star$ = 10.73

445626
$M_\star$ = 10.95

446665
$M_\star$ = 10.51

447914
$M_\star$ = 10.97

448830
$M_\star$ = 11.02

452031
$M_\star$ = 10.97

452978
$M_\star$ = 10.94

454171
$M_\star$ = 10.77

454172
$M_\star$ = 10.56

456326
$M_\star$ = 10.99

458470
$M_\star$ = 11.01

459557
$M_\star$ = 10.45

461785
$M_\star$ = 11.07

462710
$M_\star$ = 10.94

464163
$M_\star$ = 10.86

465255
$M_\star$ = 10.79

467415
$M_\star$ = 10.96

468590
$M_\star$ = 11.02

469487
$M_\star$ = 10.75

470345
$M_\star$ = 10.92

471248
$M_\star$ = 10.93

471996
$M_\star$ = 10.85

472548
$M_\star$ = 10.88

473329
$M_\star$ = 10.93

474008
$M_\star$ = 10.82

475016
$M_\star$ = 10.96

475619
$M_\star$ = 10.96

476266
$M_\star$ = 10.58

477328
$M_\star$ = 10.69

478216
$M_\star$ = 10.66

479290
$M_\star$ = 10.85

479938
$M_\star$ = 10.69

482155
$M_\star$ = 10.97

482889
$M_\star$ = 10.83

483594
$M_\star$ = 10.81

485056
$M_\star$ = 10.82

487742
$M_\star$ = 10.45

488530
$M_\star$ = 10.96

489206
$M_\star$ = 10.84

490079
$M_\star$ = 10.61

490814
$M_\star$ = 10.57

491426
$M_\star$ = 10.84

492876
$M_\star$ = 10.84

493433
$M_\star$ = 10.69

494011
$M_\star$ = 10.76

494709
$M_\star$ = 10.78

496186
$M_\star$ = 10.69

497557
$M_\star$ = 10.55

498522
$M_\star$ = 10.88

499704
$M_\star$ = 10.59

500577
$M_\star$ = 10.42

501208
$M_\star$ = 10.82

501725
$M_\star$ = 10.79

502371
$M_\star$ = 10.60

502995
$M_\star$ = 10.80

503437
$M_\star$ = 10.73

503987
$M_\star$ = 10.63

504559
$M_\star$ = 10.60

505100
$M_\star$ = 10.60

505586
$M_\star$ = 10.93

506720
$M_\star$ = 10.79

507784
$M_\star$ = 10.40

508538
$M_\star$ = 10.41

509091
$M_\star$ = 10.62

510273
$M_\star$ = 10.82

510585
$M_\star$ = 10.56

511303
$M_\star$ = 10.53

511920
$M_\star$ = 10.80

512425
$M_\star$ = 10.55

513845
$M_\star$ = 10.76

514272
$M_\star$ = 10.41

514829
$M_\star$ = 10.78

515296
$M_\star$ = 10.70

515695
$M_\star$ = 10.90

516101
$M_\star$ = 10.54

517271
$M_\star$ = 10.64

517899
$M_\star$ = 10.88

518682
$M_\star$ = 10.60

519311
$M_\star$ = 10.87

520885
$M_\star$ = 10.56

521429
$M_\star$ = 10.51

521803
$M_\star$ = 10.53

522530
$M_\star$ = 10.70

522983
$M_\star$ = 10.70

523548
$M_\star$ = 10.75

523889
$M_\star$ = 10.64

525533
$M_\star$ = 10.47

526029
$M_\star$ = 10.39

526478
$M_\star$ = 10.50

527309
$M_\star$ = 10.51

528322
$M_\star$ = 10.50

528836
$M_\star$ = 10.59

529365
$M_\star$ = 10.68

530330
$M_\star$ = 10.67

530852
$M_\star$ = 10.62

531320
$M_\star$ = 10.37

531910
$M_\star$ = 10.63

532301
$M_\star$ = 10.59

532760
$M_\star$ = 10.66

534628
$M_\star$ = 10.67

535050
$M_\star$ = 10.48

535410
$M_\star$ = 10.68

535774
$M_\star$ = 10.61

536146
$M_\star$ = 10.40

536654
$M_\star$ = 10.38

537236
$M_\star$ = 10.70

537488
$M_\star$ = 10.49

537941
$M_\star$ = 10.64

538370
$M_\star$ = 10.42

538905
$M_\star$ = 10.63

539333
$M_\star$ = 10.64

539667
$M_\star$ = 10.39

540082
$M_\star$ = 10.61

540452
$M_\star$ = 10.52

540920
$M_\star$ = 10.53

541218
$M_\star$ = 10.52

541497
$M_\star$ = 10.59

541847
$M_\star$ = 10.45

542252
$M_\star$ = 10.50

542662
$M_\star$ = 10.36

543114
$M_\star$ = 10.67

543376
$M_\star$ = 10.73

543729
$M_\star$ = 10.61

544001
$M_\star$ = 10.43

544408
$M_\star$ = 10.51

544697
$M_\star$ = 10.41

545437
$M_\star$ = 10.51

546114
$M_\star$ = 10.50

546474
$M_\star$ = 10.56

546870
$M_\star$ = 10.44

547293
$M_\star$ = 10.62

547844
$M_\star$ = 10.61

549516
$M_\star$ = 10.50

550149
$M_\star$ = 10.55

550475
$M_\star$ = 10.38

550934
$M_\star$ = 10.42

552414
$M_\star$ = 10.66

552581
$M_\star$ = 10.54

553837
$M_\star$ = 10.47

554189
$M_\star$ = 10.38

554523
$M_\star$ = 10.45

554798
$M_\star$ = 10.61

555013
$M_\star$ = 10.34

555287
$M_\star$ = 10.52

555601
$M_\star$ = 10.52

557721
$M_\star$ = 10.47

559036
$M_\star$ = 10.39

559386
$M_\star$ = 10.49

560751
$M_\star$ = 10.48

561676
$M_\star$ = 10.45

563732
$M_\star$ = 10.42

565089
$M_\star$ = 10.44

565251
$M_\star$ = 10.43

566365
$M_\star$ = 10.43

567382
$M_\star$ = 10.43

569251
$M_\star$ = 10.54

571454
$M_\star$ = 10.46

571633
$M_\star$ = 10.54

572328
$M_\star$ = 10.51

572840
$M_\star$ = 10.42

574037
$M_\star$ = 10.32

575356
$M_\star$ = 10.39

576516
$M_\star$ = 10.39

577372
$M_\star$ = 10.39

580250
$M_\star$ = 10.41

580406
$M_\star$ = 10.41

588831
$M_\star$ = 10.41

613192
$M_\star$ = 10.51
Each of these cutouts contains all particle-level fields present in the original snapshot files (full snapshots). This release also provides additional quantities for the galaxies under focus, and these additional fields are listed and described below. They are organized by particle type, with the usual conventions (PartType0 is gas cells, PartType1 is DM particles, PartType3 is tracers, PartType4 is stars and wind particles, and PartType5 is SMBHs):
| Dataset | Shape | Units | PartType(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SubfindID | N | - | all | The Subfind ID of the subhalo that a given particle/cell belongs to, at this snapshot. This ID indexes the Subfind/Subhalo catalog of the whole TNG50 simulation. It is set to -1 if the particle/cell does not belong to any subhalo. |
| MainSnapshotIndex | N | - | all | Index into the main snapshot file(s) of this particular particle/cell. This is useful if one wants to load data from one of the post processing quantities that are available online but are not included in these cutouts (int64). |
| RotatedCoordinates | N,3 | $\rm{ckpc/h}$ | all | Spatial position of each particle/cell in the reference system of the main galaxy: a coordinate transformation is first performed to shift to the frame of reference of the (centre of the) main galaxy (SubhaloPos); thus a rotation by diagonalizing the moment of inertia tensor of stars/star-forming gas within once/twice the stellar half mass radius, such that the galaxy minor axis is oriented along the z-axis (i.e. projecting along the z-axis direction gives a face-on view). |
| RotatedCenterOfMass | N,3 | $\rm{ckpc/h}$ | PartType0 | Spatial position of the center of mass of each gas cell, after having applied the translation+rotation transformation as for RotatedCoordinates. |
| RotatedVelocities | N,3 | $\rm{km/s} \sqrt{a}$ | all | Spatial velocity of each particle/cell in the reference system where the main galaxy is at rest: a velocity transformation is first performed with respect to the bulk/peculiar velocity of the main galaxy through the simulated volume (SubhaloVel). Then the same rotation is applied as for RotatedCoordinates. |
| RotatedMagneticField | N,3 | see docs | PartType0 | Magnetic field strength of each gas cell after having applied the transformation (rotation only) as for RotatedCoordinates. |
| MH | N | $10^{10} \rm{M}_\odot / h$ | PartType0 | Total neutral hydrogen mass of each gas cell. Equals the sum of the mass of atomic HI plus molecular H2: $M_H = M_{HI} + M_{H2}$. |
| MH2_GK | N | $10^{10} \rm{M}_\odot / h$ | PartType0 | Molecular hydrogen mass of each gas cell, according to the "GK" (Gnedin & Kravtsov 2011) physical model. Note that the total neutral hydrogen (HI) mass of each cell can then be obtained as $M_{HI} = M_{H} - M_{H2}$. Based on the modeling of Popping+ (2019). |
| MH2_BR | N | $10^{10} \rm{M}_\odot / h$ | PartType0 | Molecular hydrogen mass, as above, but using the "BR" (Blitz & Rosolowsky 2006) physical model. |
| MH2_KMT | N | $10^{10} \rm{M}_\odot / h$ | PartType0 | Molecular hydrogen mass, as above, but using the "KMT" (Krumholz 2013) physical model. |
| SubfindIDAtFormation | N | -- | PartType4 | The Subfind ID of the subhalo i.e. galaxy in which the stellar particle first appeared; -1 if it was formed outside of any subhalo. |
| SnapNumAtFormation | N | -- | PartType4 | Snapshot number in which the stellar particle first appeared. |
| InSitu | N | -- | PartType4 | Has a value of 1 if the stellar particle was formed in situ, or 0 if it was formed ex situ, and -1 if it does not currently belong to any subhalo. A stellar particle is considered to have been formed in situ if the subhalo in which it was formed lies along the "main branch" of the subhalo in which the stellar particle is currently found. This is decided using the SubLink "baryonic" merger trees. |
| AfterInfall | N | -- | PartType4 | Has a value of 1 if the subhalo in which the stellar particle first appeared had already "infalled" into the halo (FoF group) where it is currently found; 0 otherwise; -1 if not applicable i.e., if the particle was formed in situ or if it was formed outside of any subhalo. |
| AccretionOrigin | N | -- | PartType4 | This dataset can take the following integer values: 0, 1, and 2 for ex-situ stellar particles that were accreted from completed mergers (i.e., when the subhalo in which the stellar particle formed has already merged with the current subhalo), ongoing mergers (i.e., when the subhalo in which the stellar particle formed has not yet merged with the current subhalo, but will do so at a later snapshot in the simulation), and flybys (i.e., when the subhalo in which the stellar particle formed has not merged with the current subhalo, and will not do so at any future snapshot in the simulation), respectively; and -1 if not applicable i.e., if the particle was formed in situ or if it was formed outside of any subhalo. |
| DistanceAtFormation | N | -- | PartType4 | The galactocentric distance when the stellar particle was formed, given in units of the stellar half-mass radius of the parent galaxy at the formation time. |
| SnapNumAtStripping | N | -- | PartType4 | The snapshot in which the stellar particle last switched galaxies, and has hence remained in its present galaxy -- i.e. time of last stripping. This field is -1 for all in-situ stellar particles and for particles that aren't part of any subhalo. |
| ProgGalaxyMassAtStripping | N | $10^{10} \rm{M}_\odot / h$ | PartType4 | Total stellar mass (as identified by Subfind) of the secondary progenitor galaxy of this stellar particle, from snapshot SnapNumAtStripping - 1. |
| ProgGalaxyMassInRadAtStripping | N | $10^{10} \rm{M}_\odot / h$ | PartType4 | As above, but for the stellar mass within twice the stellar half mass radius of the secondary progenitor galaxy. |
| ProgSubhaloMassAtStripping | N | $10^{10} \rm{M}_\odot / h$ | PartType4 | As above, but for the total subhalo mass of the secondary progenitor galaxy, i.e. the sum of all gravitationally-bound mass. |
| DistanceToHostAtStripping | N | $ckpc / h$ | PartType4 | Distance to the centre of the primary galaxy at snapshot SnapNumAtStripping. Here, the centre of the galaxy refers to the position of the most-bound particle of PartType = 4). |
| Xray_Emission_03_2keV | N | $\rm{erg\ cm^3/s}$ | PartType0 | Intrinsic and instantaneous X-ray emission of the gas in the soft broad band [0.3-2] keV. This includes contributions from both the continuum and the lines and is given as X-ray cooling rate. The cooling rate is physically similar to the gas field GFM_CoolingRate. To compute the luminosity of a cell: $L_{\rm X} \rm{[erg/s]} = \rm{CoolingRate} \times n_{\rm e} \rm{[cm^{-3}]} \times n_{\rm H} \rm{[cm^{-3}]} \times V \rm{[cm^3]}$, where $n_{\rm e}$ and $n_{\rm H}$ are hydrogen and electron number densities, and $V$ is the volume of the gas cell. It is computed assuming an emission model APEC from the XSPEC package using the element abundances traced by the simulation (using the VAPEC model in the XSPEC package). Available only at the $z=0$ snapshot. Based on Truong+ (2023). |
| Xray_Emission_05_2keV | N | $\rm{erg\ cm^3/s}$ | PartType0 | As above, but for the [0.5-2] keV band. |
| Xray_Emission_03_2keV_C | N | $\rm{erg\ cm^3/s}$ | PartType0 | Same as Xray_Emission_03_2keV, except including only continuum emission only (no line emission). |
| Xray_Emission_05_2keV_C | N | $\rm{erg\ cm^3/s}$ | PartType0 | Same as Xray_Emission_05_2keV, except including only continuum emission only (no line emission). |
| Xray_Emission_Line_{linename} | N | $\rm{erg\ cm^3/s}$ | PartType0 | Intrinsic and instantaneous X-ray emission of the gas (as in Xray_Emission_03_2keV) in narrow bands at nine specific lines, with {linename} = CV (298.97 eV), CVI (367.47 eV), NVI (419.86 eV), NVII (500.36 eV), OVIIf (560.98 eV), OVIIr (573.95 eV), OVIII (653.49 eV), FeXVII (725.05 eV), and NeX (1021.5 eV). Based on Truong+ (2023). |
The PartType4 entries above are part of the "Stellar Assembly" catalog, and are all based on
Rodriguez-Gomez+ (2016).
The cutout headers contain a subset of information from the header of the main snapshot files. In addition there are two added entries:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SubfindID_This_Snapshot | The Subfind ID of the (progenitor) subhalo in this snapshot. |
| TracerLength | An array of [NumTracersGas, NumTracersStars, NumTracersBH]. In these snapshot cutouts,
only those tracers are stored that "reside" in cells/particles that are included in the cutout. Tracers
are ordered based on the particles they reside in, i.e. all tracers in gas cells (a total of
NumTracersGas) are stored first, followed by those in stars (NumTracersStars),
and finally BHs (NumTracersBH). The TracerLength array can be used to quickly
load only a subset of tracers, if required. For example, only those tracers that currently reside in gas
cells can be quickly selected by only loading the first NumTracersGas entries. Since
particles/cells can leave/enter the cutouts over time, these tracer cutouts are mainly useful
for short time-scale phenomena analysis. |
Cosmological Cloud Catalog (HVC and IVC analogs)
In Ramesh+ (2023b) we identified tens of thousands of small, cool gas clouds in the circumgalactic medium (CGM) of the Milky Way-like galaxies of this sample. The resulting Cosmological Cloud Catalog is publicly available, and contains extensive measurements of the physical properties of these clouds.
TNG50 Papers Studying the MW/M31 Sample
| Paper | Topic |
|---|---|
| Pillepich+ (2024) | overall introduction |
| Engler+ (2021b) | abundance of satellites |
| Pillepich+ (2021) | X-ray eROSITA-like CGM bubbles |
| Gargiulo+ (2022) | stellar bulges and bars |
| Sotillo-Ramos+ (2022) | disk survival through mergers |
| Carollo+ (2022) | formation of very metal-poor disky stars |
| Engler+ (2022) | star formation and gas contents of satellites |
| Ramesh+ (2023a) | properties of the CGM |
| Chen+ (2023) | location of extremely metal-poor stars |
| Ramesh+ (2023b) | high-velocity/cold clouds in the CGM |
| Sotillo-Ramos+ (2023) | flaring of the stellar disk |
| Bisht+ (in prep) | stellar radial migration |
| Sotillo-Ramos+ (in prep) | ex-situ disks |
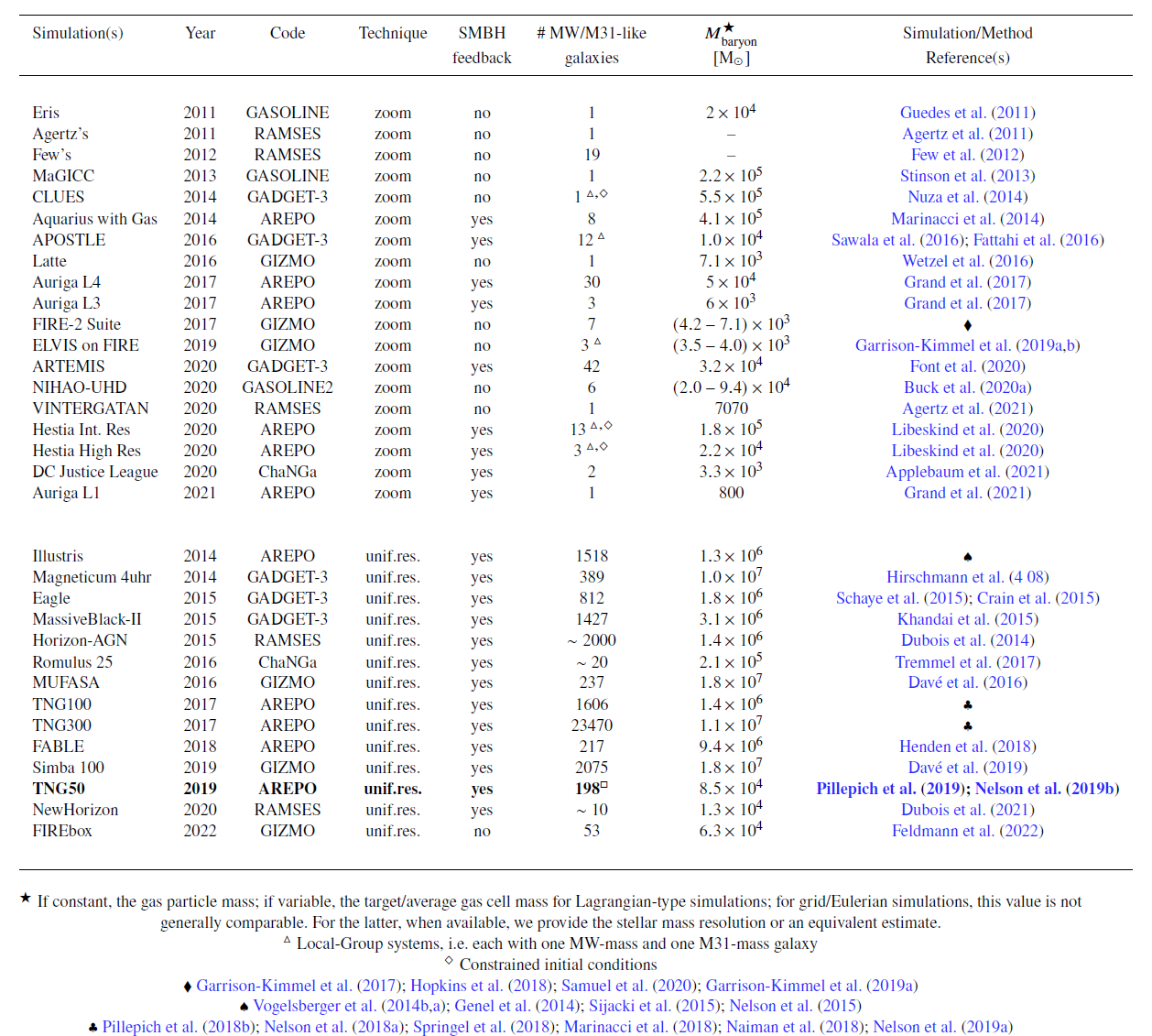
Landscape of $\Lambda\rm{CDM}$ Simulations of MW/M31 Analogs
Cosmological (magneto-)hydrodynamical simulations of MW/M31-like galaxies or Local Group-like (LG) systems in a $\Lambda\rm{CDM}$ scenario} currently pursued by the community. The list deliberately omits idealized and isolated-disk simulations, dark-matter only simulations -- even if they have paved the road for the subsequent hydrodynamical ones, especially in the context of MW-mass haloes --, and cosmological simulations with too poor resolution for galaxies and their stellar disks to be studied. Namely, here we include only cosmological models, i.e. simulations that start from cosmologically-motivated initial conditions on $\gg$ 10s Mpc scales, which are run to $z=0$. We hence also list large-volume uniform-resolution projects (specifically those with baryonic mass resolution better than a few $10^7 \rm{M}_\odot$), as they naturally include MW/M31-mass galaxies.